Ethereum Sharding 101: What Is It & How It Works?

ethereum
All blockchain networks have always struggled with a blockchain trilemma. So far, none of them has managed to be secure, decentralized, and scalable at the same time; one of the traits has always been sacrificed in favor of the remaining two. To tackle the scalability issue, the Ethereum network has come up with an ingenious solution: Ethereum sharding.
What Ethereum sharding is, what its pros and cons are, and how it improves the scalability of the network is explained in our latest guide. Keep reading to find it out!
What Is Sharding?
Sharding stands for breaking a blockchain network into multiple components referred to as shards. Every shard holds a unique subset of transactional data and runs its own smart contracts; as such, it’s capable of processing transactions on its own.
The concept of sharding emerged about thirty years ago as a database management system. The term SHARD is an acronym for System for Highly Available Replicated Data, a database product of the 1980s. But why is sharding essential for blockchains, given the fact that blockchain technology is way more modern than that of the 1980s?
To validate a transaction, a blockchain network relies on the so-called nodes. The more nodes the network requires, the more limited its ability to scale is. Greater scalability, i.e., the capacity to process a large number of transactions, is necessary for the mass adoption of blockchain technology.
Splitting the main blockchain into smaller segments enables nodes to verify a smaller subset of transactions in parallel. This way, network throughput increases, enabling dApps to scale and satisfy the needs of the growing number of users.
What Is Sharding in Ethereum?
Ethereum is known for its capacity to process up to 30 transactions per second (TPS). Compared to centralized systems like VISA or PayPal, which can process 24,000 and 163 TPS, that figure is way too low. Plus, in periods of high activity, that number can drop significantly, taking more time to verify and process transactions.

With sharding, Ethereum’s throughput is projected to jump to 100,000 TPS. The precise number of transactions per second may vary until the process of sharding is completed and fully implemented on the network. Still, it’s undoubtedly a significant improvement compared to the current throughput.
Another issue that Ethereum sharding can tackle is high gas fees. Gas stands for fees that a network user needs to pay in order to have their transaction processed on the Ethereum blockchain. Currently, the gas revolves around 25 gwei, with one gwei equaling one billionth of an ETH.
Gas fees on Ethereum can be extremely volatile, depending on network demand. During periods of high activity, the network can become congested, urging users to give generous tips so that their transactions are executed more urgently. All this results in driving gas fees up so that they reach unfathomable amounts of ETH.
Ethereum sharding could help lower the overall price of gas by reducing competition for resources. This way, not only will transactions be executed faster, but they will also be cheaper.
How Does Ethereum Sharding Work?
As we’ve already mentioned, Ethereum sharding involves splitting the network into shards, each of which holds a subset of smart contracts, transactions, and accounts. All transactions are processed and stored on the shard where they occur instead of the network itself.
Every shard possesses a set of validators that allow them to process transactions simultaneously across multiple shards. This model eases the burden imposed on the entire network by processing segments of Ethereum transactions in smaller shards.
As is the case with the whole network, validators are accountable for the maintenance and transaction verification on a shard. To become a validator, network participants need to stake a specific amount of ETH. The higher their stake is, the better their prospects of being chosen to validate transactions are.
Here’s a visual representation of a sharded Ethereum:
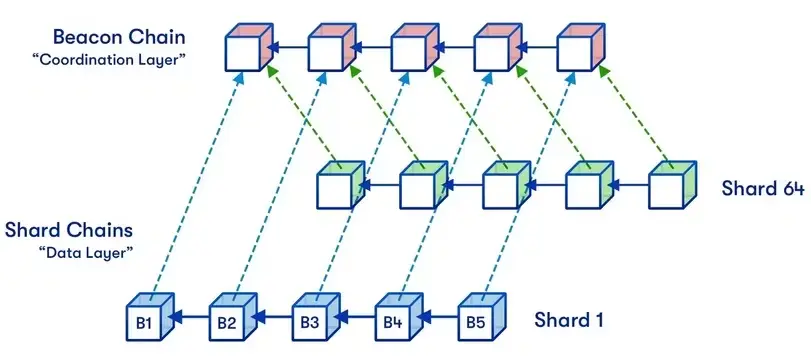
Source: @VitalikButerin
As a reminder, Ethereum has switched from the proof-of-work (PoW) to the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism to ensure the security of the blockchain. This was the beginning of Ethereum’s path to better scalability, security, and sustainability for the network.
Ethereum sharding was seen as the core of the second stage, referred to as the Surge, whose goal is to improve scalability. The most efficient way to achieve this is via layer-2 rollups and EIP-4844, also known as proto-Danksharding.
This is a step toward the final stage of the Ethereum sharding roadmap called Danksharding. Yet, before reaching this stage, the network will need to implement a few Ethereum sharding upgrades.
Ethereum Sharding Key Components
Here are the key components of Ethereum sharding:
#1. Decentralized Nodes
Ethereum sharding enables anyone to run a node. However, rather than expanding the existing databases, which may lead to centralization, sharding lets the Ethereum network scale while remaining decentralized.
A scaled network with a significantly large database would impose strict technical requirements in terms of expensive equipment on validators. This would further lead to high electricity bills and maintenance costs. Eventually, such a system may allow centralization to sneak in due to extremely high entry barriers.
Sharding, however, may not expect validators to keep all the network data on their computers. Instead, techniques like zero-knowledge rollups may be implemented to confirm if data is available on the network.
#2. Increased Participation
This is one of the long-term benefits of sharding. As the Ethereum network will manage to scale securely, the ultimate objective is to let people run Ethereum on their laptops or smart devices.
Running clients will become more accessible and attract more users across the globe. This circles back to decentralization and security, considerably reducing the chance of a failure or attack.
#3. Improved Performance and Efficiency.
Sharding will boost the speed and throughput of the Ethereum network as the processing of transactions will not be restricted to a single chain. It is believed that sharding may lead to a growing number of TPS on the network, making it similar to centralized payment systems such as VISA or PayPal.
The Importance of Ethereum Sharding
Blockchain networks can process only a limited number of transactions at a time. The reason for this lies in the fact that nodes have to verify a transaction before it can be processed. Each node holds the entire history of the blockchain, preventing malicious actors from modifying or retrieving a transaction. Such a way of keeping the network secure and decentralized sacrifices its scalability.
Sharding allows nodes to bypass downloading the entire history of the blockchain or validating every single transaction that enters the network. This way, the network’s performance is improved, enabling the blockchain to deal with a larger number of users.
All this further leads to improved scalability, which is by far the most significant advantage of sharding. Owing to greater scalability, the blockchain can store a larger amount of information and link extra nodes without slowing down transaction times.
Hitting the projected 100,000 TPS would make Ethereum a convenient payment method. Plus, blockchain technology can be implemented across various industries at a quicker rate. More businesses would be able to select the fast and secure transactions provided by the network.
Benefits of Ethereum Sharding
In addition to enhancing scalability and reducing gas fees, Ethereum sharding has a few other benefits. The most important of them include but are not limited to:
#1. Increased Throughput
By breaking down the blockchain network into shards, Ethereum can obtain a better throughput, processing more transactions per second. This will further improve the entire scalability of the network and allow it to process far more transactions per second.

This, in turn, will make the blockchain more convenient for a wide range of applications, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) or non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
#2. Improved Security
Ethereum sharding maintains security by implementing cross-link implementation between shards and the primary chain. This makes sure the network's security isn’t compromised in spite of the decentralized transaction processing across the shards.
The security of the network is of considerable importance for Ethereum, as it makes it a trustworthy platform for smart contracts and decentralized applications.
#3. Sustainability and the Use of Resources
Once the blockchain is divided into multiple shards, all the workload is distributed to them. This instantly improves transaction processing and increases throughput; plus, it contributes to the overall sustainability of the Ethereum network.
As the demand for Ethereum applications increases, sharding prevents excessive energy consumption and network congestion by allowing the network to scale sustainably.
#4. Solving the Blockchain Trilemma
Not a single blockchain has managed to have decentralization, security, and scalability; one of the three has always been sacrificed. Thanks to sharding, Ethereum may be the first to include all three and become a highly scalable, secure, and decentralized network.
Cons of Ethereum Sharding
Sharding has its challenges, too, the greatest one being that it hasn’t been put into practice. In fact, the Ethereum sharding release date was planned for sometime in 2023, but to date, nothing has been officially released yet. What’s more, there isn’t a set Ethereum sharding timeline, so we may hope to see it sometime in 2024.
The key reason for this lies in the fact that sharding is an extremely complicated process. It certainly sounds like a fantastic idea that, in theory, may have promising implications. Yet, specific risks, such as potential attack vectors, can hinder its adoption.
One such dangerous challenge is a so-called single-shard takeover attack. Here, the attacker may take control over a major portion of block producers in a shard and start creating malicious shards to submit invalid transactions.
Another challenge is cross-shard communication. Transactions that include a greater number of shards need to communicate efficiently. Such strong communication may not seem unattainable in theory, but in practice, it can be difficult to implement it effectively.
Shard security may be a huge challenge as well. Every shard is accountable for maintaining its own security. Yet, it might be difficult to attain without compromising the security of the entire network.
The Ethereum network boasts its functionality owing to smart contracts. However, in the case of sharding, smart contract compatibility may come across as a considerable challenge since it would require developers to modify and adapt codes to the new system. Incompatibility may emerge if there is no upgrade option, making the execution of the code challenging.
Key Takeaways
Ethereum sharding emerges as an up-and-coming solution to the notorious scalability issue that the network is facing. Splitting the blockchain into smaller portions, i.e., shards, enables Ethereum to process more than up to 30 transactions per second. Plus, it would help improve the overall efficiency of the network without sacrificing its decentralization.
However, due to the complexity and challenges it faces, Ethereum sharding hasn’t been released to date. We hope to see it sometime in 2024, as it would be a huge improvement for the network.
Ethereum sharding might revolutionize not only the network itself but the entire blockchain industry. If implemented successfully, it can offer a strong foundation for the future of smart contracts and dApps.